Characterizing quantitative literacy tasks
There are 33 tasks ordered along the IALS 500-point quantitative literacy scale. These
tasks range in difficulty value from 225 to 409. The easiest quantitative literacy task
(with a difficulty value of 225) directs the reader to complete an order form. The last
line on this form says, "Total with Handling."
The line above it says, "Handling Charge
$2.00."
The reader simply had to add the $2.00 to the $50.00 they had entered on a
previous line to indicate the cost of the tickets. In terms of our process variables, this
item received a code of 1. The design of the form set the problem up in simple column
format for the reader and the amount for handling was stipulated, so there was little
required of them in terms of type of match (TOM) or plausibility of distractor (POD).
In addition, the last line on the form said, "Total with Handling,"
indicating the type
of operation and the numbers did not require the reader to carry or borrow. As a result,
both type of calculation (TOC) and operation specificity (OSP) were each coded 1.
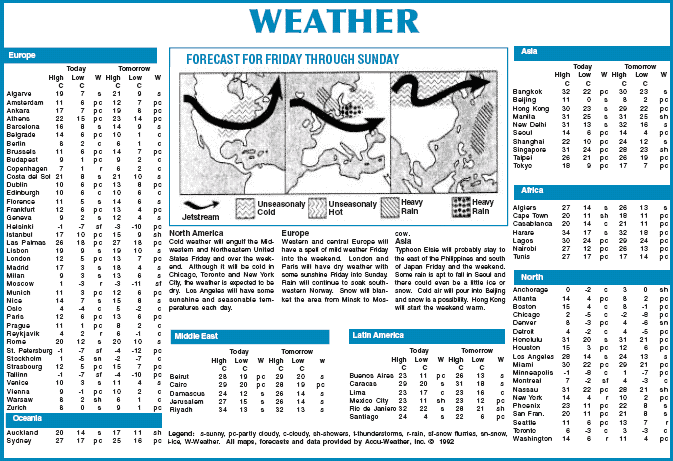
A second quantitative literacy task directs the reader to use a weather chart in a newspaper to determine how many degrees warmer today's high temperature is expected to be in Bangkok than in Seoul. This item received a difficulty value of 255. This task was made more difficult both in terms of the literacy processes and in terms of those processes associated with the quantitative scale. Here the reader had to cycle through a complex table to make two, three-feature matches to identify the two temperatures, and then subtract one from the other to determine the difference. The numbers they had to subtract were not adjacent to each other in the table, were not in column format, and had to be identified through a search. As a result, operation specificity was coded a 3, type of calculation received a 2, type of match was scored a 4, and plausibility of distractor was scored a 4.