Upon further consideration, however, we chose to expand this unidimensional model to more fully represent the complexity of ICT literacy. This organizational scheme, shown below in Figure 2, illustrates the foundational set of skills and knowledge that underlie ICT literacy: cognitive and technical proficiency.
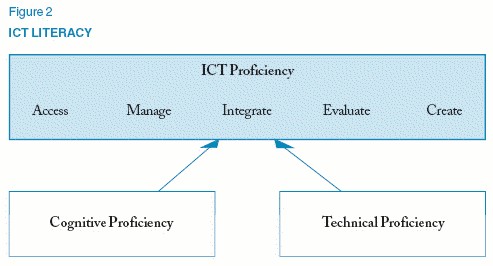
The three proficiencies are defined as follows.
- Cognitive Proficiency—the desired foundational skills of everyday life at school, at home, and at work. Literacy, numeracy, problem solving, and spatial/visual literacy demonstrate these proficiencies.
- Technical Proficiency—the basic components of digital literacy. It includes a foundational knowledge of hardware, software applications, networks, and elements of digital technology.
- ICT Proficiency—the integration and application of cognitive and technical skills. ICT proficiencies are seen as enablers; that is, they allow individuals to maximize the capabilities of technology. At the highest level, ICT proficiencies result in innovation, individual transformation, and societal change.