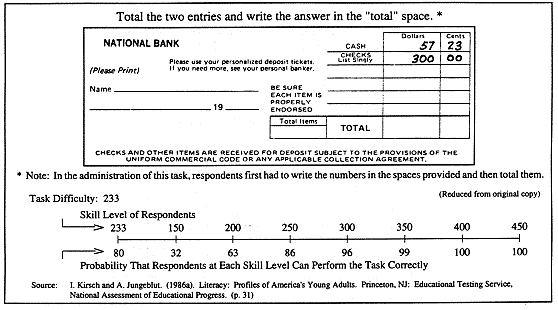
* This item was also used in the 1992 National Adult Literacy Survey (NALS). This Quantitative literacy task has a difficulty level of 233, meaning that people must possess a skill level of 233 to have an 80% probability of being able to perform the task correctly. On the Quantitative scale, the YALS report states that, over all items,
99.6 percent perform at the 150 level or
above, On the Quantitative literacy scale, the overall percent correct was 65. Whites scored an average of 68.9%, Hispanics 57.8% and Blacks 45.8% correct. Only 47% of the Quantitative literacy tasks were at or below a difficulty level of 300. This contrasts with the Document literacy scale where 73% of the tasks were at or below the 300 level of difficulty. On the Quantitative scale, there were no tasks below a difficulty level of 250. Despite this, the theoretical curves relating ability to the 80% probability of being able to perform tasks at different difficulty levels leads to the reported (hypothetical) finding that 96.4%, and not 100%, of young adults would perform at the 200 level or above. This occurs even when there are, in fact, no items at the 150 or 200 levels. Note: In the assessment of Job Training Partnership Act (JTPA) opportunities and job seekers using the Unemployment Insurance (UI) systems, this item required "the reader to enter and total two numbers "on the bank deposit slip." It is cited as having a difficulty level of 226 (I. Kirsch, A. Jungeblut, and A. Campbell, (1992, September). Beyond the School Doors: The Literacy Needs of Job Seekers Survival by the U.S. Department of Labor. Washington, DC: U.S. Dept. of Labor, Employment Training Administration. (p.51) |
||||